In Canada (and everywhere else in the world), mortgages are what enable individuals and families to purchase homes without having to pay the full price upfront. A mortgage is basically a loan secured by real property, where the borrower agrees to repay the lender over a specified period (with interest).
There are two primary types of mortgages available in Canada: fixed-rate mortgages and variable-rate mortgages. Choosing between fixed and variable is not an easy decision to make, because it can impact your financial situation for many years. You need to make that decision based on individual financial circumstances, market conditions, and personal risk.
In a nutshell, a fixed-rate mortgage provides stability with a constant interest rate, while a variable-rate mortgage offers potential savings with fluctuating rates. Fixed and variable have their own benefits and risks, and the right choice depends on various factors including financial goals and market conditions.
Fixed-Rate Mortgage Overview
How Does a Fixed-Rate Mortgage Work?
A fixed-rate mortgage is a type of home loan where the interest rate remains the same throughout the entire term of the loan. This means that the monthly mortgage payments stay the same, which is good when it comes to providing consistency for the borrower.
In Canada, typical loan terms for fixed-rate mortgages range from 5 to 15 years. Longer terms may also be available, depending on the bank. The fixed-rate mortgage is popular among Canadian homeowners who prefer consistency and the ability to plan their finances without worrying about fluctuating interest rates.
Once the interest rate is set at the beginning of the loan term, it doesn’t change. So, even if there are changes in the market interest rates, your payments would remain the same. Those planning for the long term and wanting to avoid the uncertainty that comes with fluctuating interest rates will benefit the most from this.
Types of Fixed-Rate Mortgages
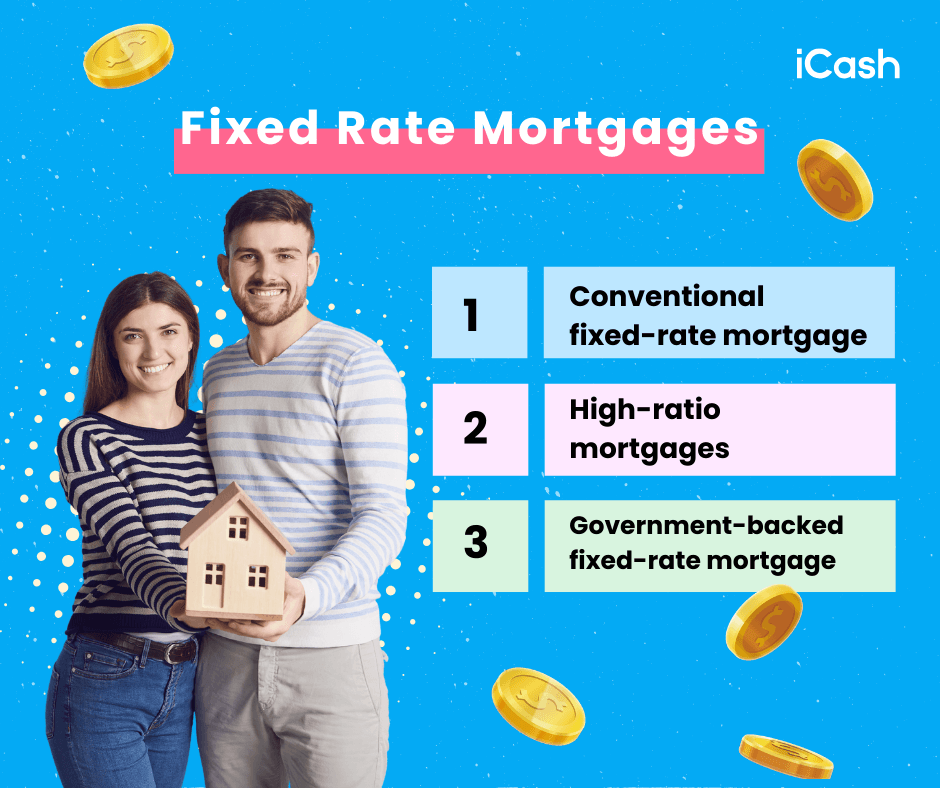
There are several types of fixed-rate mortgages available in Canada, each with different features that’ll appeal to different people, depending on their financial situation:
A conventional fixed-rate mortgage requires a down payment of at least 20% of the home's purchase price. The fixed rate mortgage loan amount does not exceed 80% of the property's value. If the borrower has a good credit score and a stable income, conventional fixed-rate mortgages are easier to qualify for.
Then there are high-ratio mortgages, which are for borrowers who make a down payment of less than 20%. High-ratio mortgages require mortgage default insurance, which protects the lender if the borrower defaults on the loan. This type of fixed rate mortgage allows people with smaller down payments to purchase a home, but it usually comes with the additional cost of mortgage insurance.
A government-backed fixed-rate mortgage is one that is insured by government entities like the Canada Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC). The terms might be a bit more flexible and easier to qualify for, especially for first-time homebuyers. They might come with benefits like lower down payment requirements and more lenient credit score criteria.
Each one is unique and caters to different financial situations and goals. Understanding the specific requirements and benefits of each can help you choose the best fixed rate mortgage option for your needs.
Benefits and Risks of Fixed-Rate Mortgages
Benefits
Stable Monthly Mortgage Payments: Fixed-rate mortgages provide consistent monthly payments, making it easier to budget and plan finances. This predictability is one of the main attractions of fixed-rate mortgages, especially for those with a fixed income.
Protection Against Fluctuating Interest Rate: Borrowers are protected from potential increases in the interest rate over the term of the mortgage. This means that even if the market rates go up, your interest rate would remain unchanged.
Easier Budgeting: With consistent payments, it’s easier to manage monthly expenses and avoid financial surprises, especially for those who prefer a morr conservative approach to their finances.
Risks
Potentially Higher Initial Interest Rates: Fixed-rate mortgages often come with higher interest rates compared to variable-rate mortgages. This means higher initial payments, which can be a drawback for some borrowers.
Less Flexibility if the Interest Rate Drops: If the markets change and interest rates decrease, you’ll be locked into your original interest rate and may end up missing out on saving money. You can always choose to refinance the mortgage to take advantage of lower rates, but it may involve additional costs and fees.
Variable-Rate Mortgage Overview
How Does a Variable-Rate Mortgage Work?
A variable-rate mortgage, also known as an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM), has an interest rate that changes periodically based on market conditions. Variable rate mortgages in Canada are typically tied to the lender's prime rate, which can fluctuate with changes to the Bank of Canada's policy rate. Variable-rate mortgage adjustment periods may be as short as a year, as long as five years, or even longer.
Variable-rate mortgages are attractive to borrowers who are willing to take some risk in exchange for the potential benefits of lower interest rates. Variable rate mortgages usually have a lower interest rate at the beginning of the loan term. However, because the variable rate can change, so can the monthly payments.
Types of Variable-Rate Mortgages
Various types of variable-rate mortgages are available in Canada, each catering to different financial needs.
Hybrid ARMs start with a fixed interest rate for an initial period and then become variable. This variable rate option offers a combination of stability and potential savings. For example, a 5/1 ARM would have a fixed rate for the first five years, and then adjust annually after that.
With interest-only ARMs, borrowers initially pay only the interest on the variable rate mortgage loan for a certain period. Then, the payments increase to cover both principal and interest. This type of mortgage might be beneficial for anyone who expects their income to increase in the future or who plans to sell the property before the interest-only period ends.
Then you have Payment-Option ARMs which give borrowers the option of multiple payment options each month, including interest-only payments, minimum payments, etc. This flexibility can help manage cash flow but can also lead to negative amortization (which is when the amount you owe still goes up because you’re not paying enough to cover the interest), which can be a dangerous financial position to be in.
Benefits and Risks of Variable-Rate Mortgages
Benefits
Lower Initial Interest Rates: Variable-rate mortgages often start with lower interest rates compared to fixed-rate mortgages, which is great because it can make homeownership more affordable at first, especially for first-time buyers.
Potential for Lower Mortgage Payments: Borrowers may benefit from lower monthly payments with a variable rate mortgage if the market interest rates decrease. This can help you save a bit of money over the life of the loan.
Risks
Uncertainty in Monthly Mortgage Payments: The interest rate on a variable-rate mortgage can increase and lead to higher monthly payments, which for some, means potential financial strain.
Potential for Higher Payments: There’s always the risk that the mortgage interest rate rises significantly on a variable-rate mortgage. If that happens borrowers would end up facing a much higher monthly payment than anticipated, which can lead to financial difficulties.
Difficulty in Budgeting: If payments end up increasing on your variable-rate mortgage, it can make it challenging for homeowners to maintain a consistent budget. This can be particularly problematic for anyone on a tight budget without any wiggle room for increased expenses.
Comparing Fixed-Rate and Variable-Rate Mortgages
To make an informed decision between a fixed-rate and variable-rate mortgage, it's important to compare the two based on several key factors. Let’s take another brief look at the main components of fixed and variable rates.
Factor | Fixed-Rate-Mortgages | Variable-Rate Mortgages |
Stability | High stability with consistent payment | Payments can fluctuate based on rates |
Flexibility | Less flexibility if rates drop | More flexibility if rates decrease |
Initial Interest Rates | Typically higher | Typically lower |
Long-Term Costs | Predictable, potentially higher | Unpredictable, potential for lower or higher |
Suitability | Ideal for those seeking stability | Suitable for those comfortable with risk and potential rate changes |
Which Mortgage Rate is Right For You?
Choosing between fixed mortgage vs variable mortgages is a significant (and somewhat difficult) decision for Canadian homebuyers to make.
When deciding between fixed vs variable, consider your financial goals, risk tolerance, and the current market conditions. For instance, if you prefer stability and have a low tolerance for risk, a fixed-rate mortgage might be the better choice. But if you’re comfortable with some risk and hoping for lower initial payments, a variable-rate mortgage could work for you.
It’s also a good idea to consult with a mortgage advisor or financial planner to understand the best option for your situation when it comes to fixed vs variable. They can help your decision-making process based on current market trends and help you figure out the long-term implications of each mortgage type. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on your personal financial circumstances and long-term plans.